The main objectives of the present dissertation is to establish and prove that apart from the empirical and theoretical preliminary design study that is usually applied in order to determine an adequate repair material for repairing reinforced concrete structures damaged by earthquakes, there is also a more advanced procedure which is accomplished by means of extensive analysis with the aid of dedicated software based on recent codes and regulations.
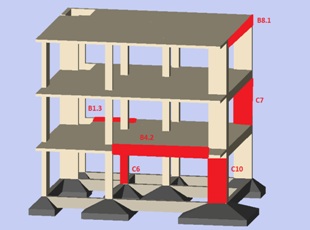
The second part includes the first stage of the software analytical component of the dissertation. With the aid of the professional design software Master 10 EC Fespa which operates primarily based on the latest editions of Eurocodes, an appropriate selected RC building located in an area with high and frequent seismic will undergo repair design analysis. At this stage the analysis will contain: i) the graphically representation of the building in the software, ii) the identification and fault type classification assignment on each of the building’s harmed elements iii) non-linear static (pushover) analysis to estimate the pre-repair structure behavior comparing the earthquake response of the building with the seismic stresses of the area, iv) the selection of the appropriate repair method for each hurt element.
The third major part contains the second stage of the software analysis. All the building data are inputted, the re-design of the under repair elements using the specified methods is taking place, and results regarding the new repaired elements design properties are generated. These properties are compared with the ones of their pre-repair state, and the significance of the findings are discussed. Finally the repaired now building will undergo pushover analysis again, so that it will be possible to compare and comment the pre-repair and post-repair behavior state, and to determine the effectiveness of the selected repair methods.
After a research like this, a wealth of theoretical information and software analysis outcomes are obtained, which in combination with personal knowledge and experience, that may be achieved after extensive study of literature, regulations and directives, could aid to the selection of an appropriate repair material and implementation method in order to achieve the maximum possible restoration-repair successfulness of the critical property (e.g. shear, bending moment) of each earthquake damaged structural element.
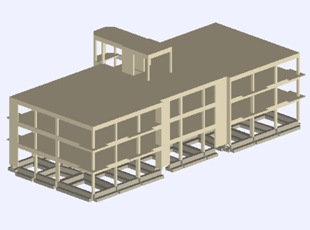
The objective of the present dissertation is the assessment of the resistance of the building and the rehabilitation of an existing reinforced concrete building by applying non Linear Static Analysis (Pushover), as defined with the relevant provisions of Eurocode. The structural system consists of moment frames and comprises a ground floor, two floors and a roof. The initial study was made in 1987 when the building was constructed.
Thereafter, the building and its analysis model are thoroughly described. Particular emphasis is given to simulate the inelastic behavior of critical sections of the structural elements.
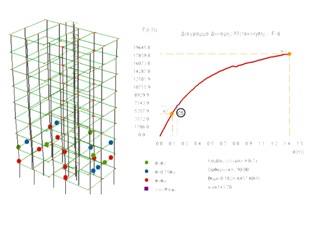
Furthermore, presented the analysis of the building with the non-linear static procedure of Eurocode 8, in order to make the assessment of the building resistance for the target design, which corresponds to performance Level “Significant Harm’, for seismic activity with 10% probability of exceedance in 50 years. The results indicate a need to strengthen a large number of beams of the building, in order to increase their flexural strength, and also a failure from a large number of walls and several columns.
For this purpose, was chosen both the strengthening of beams with fiber wrap overlays throughout their length and also the strengthening of vertical elements with a concrete sealing and construction of new walls in some panels of the body throughout its height. Moreover, an increase of the bearing capacity of the foundation by adding piles is required. Furthermore, the analysis of the reinforced body to assess the resistance of the building for the same objective planning with the incumbent is presented.
Finally, all data, assumptions and results of the analysis both at the stage of the valuation, and the rehabilitation are presented and discussed thoroughly, fully detailed for each phase of the concerned institution. Also there is a reference made to some useful conclusions relating to non-Linear Structural Analysis and arising during their implementation in practice.
The purpose of this post-graduation thesis deals with the study and research of the behavior factor “q” and its effect upon all concrete building structures that are designed by the contemporary Eurocode EC2, part 1.1 and EC8, part 1.
First of all, a general reference to the meaning of plasticity of concrete building structures is made, since plasticity relates directly to the behavior factor “q”. Consequently, the role of the behavior factor “q” is analyzed based on the linear seismic analysis and then references of the behavior factor “q” are separately displayed both by the previous Hellenic Seismic Code (EAK-2000) and the new Eurocode EC8, part 1. Finally, a qualitative and quantitative comparison of the values of the behavior factor “q” that both Regulations require is implemented.
Furthermore, the essay studies the effect of the value of behavior factor “q” upon the overall actual cost of concrete building structures. For this purpose several case studies of concrete building models are analyzed with static system variations between frame system and coupled wall system. On those building models analysis for various values of the behavior factor “q” is applied, starting from the minimum value of “q“ = 1,5 to the maximum allowable value of “q” depending on the seismic Regulation respectively. The results of the measurements of the analysis show a noticeable clear decrease of the initial building structures expenditure, specifically on building structures designed for larger values of the behavior factor “q” compared to those designed for smaller values.
In conclusion, an inquiry of the application of non-linear static analysis “Push-over” for the inspection or the reconsideration of the values of the multiplication factor αu/α1, according to which is in many cases the behavior factor “q” on building structures is determined based on the Eurocode EC8, part 1. For this purpose a framework of parametric analysis has been planned, wherein a series of non-linear “Pushover” analyses has been implemented with the use of technical software on a number of different cases as a result of the variation of a series of parameters, such as height, geometry of the floor plan (length/width ratio) and the relationship of geometrical stiffness of columns and beams.



 read more
read more





